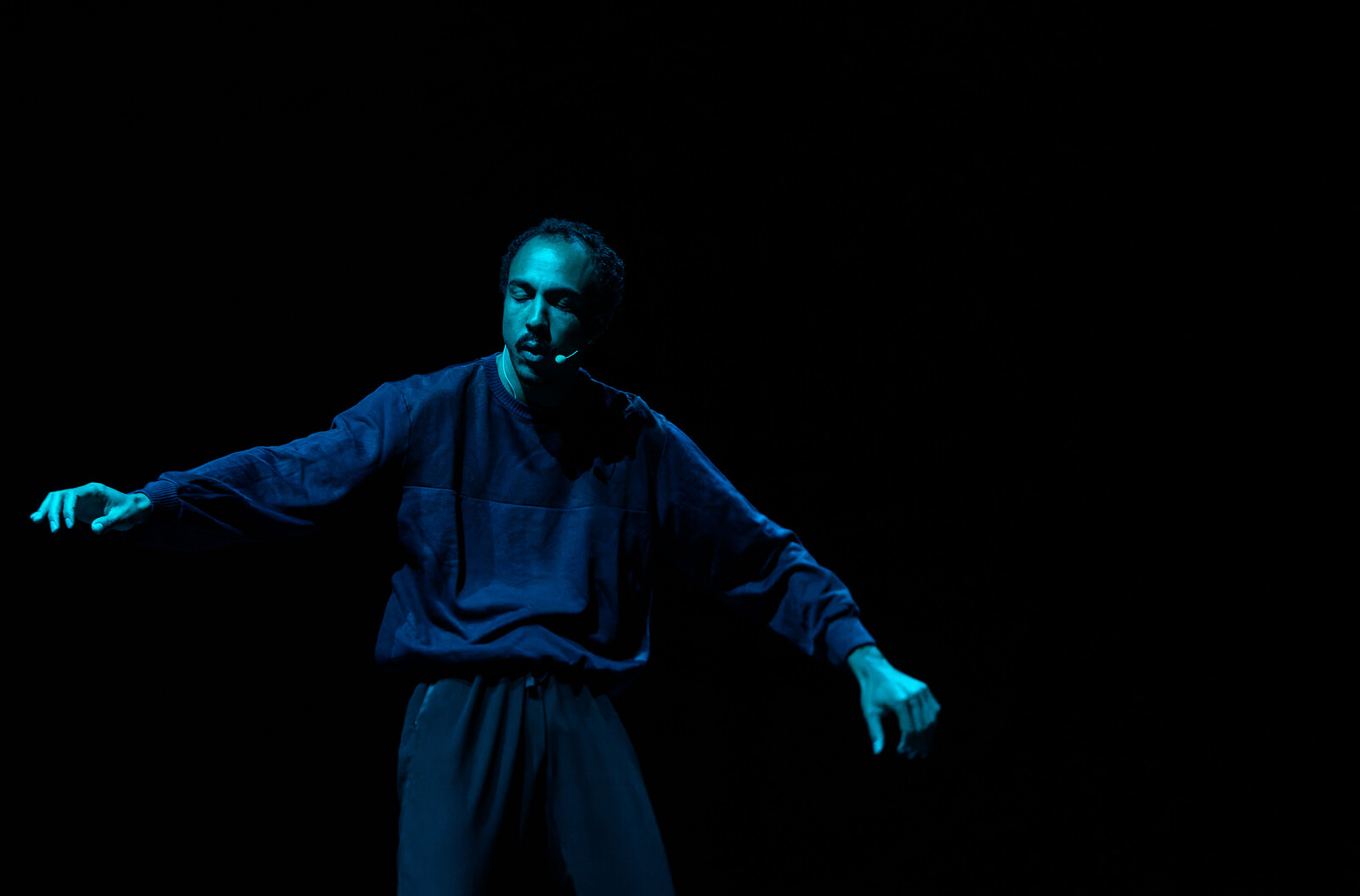
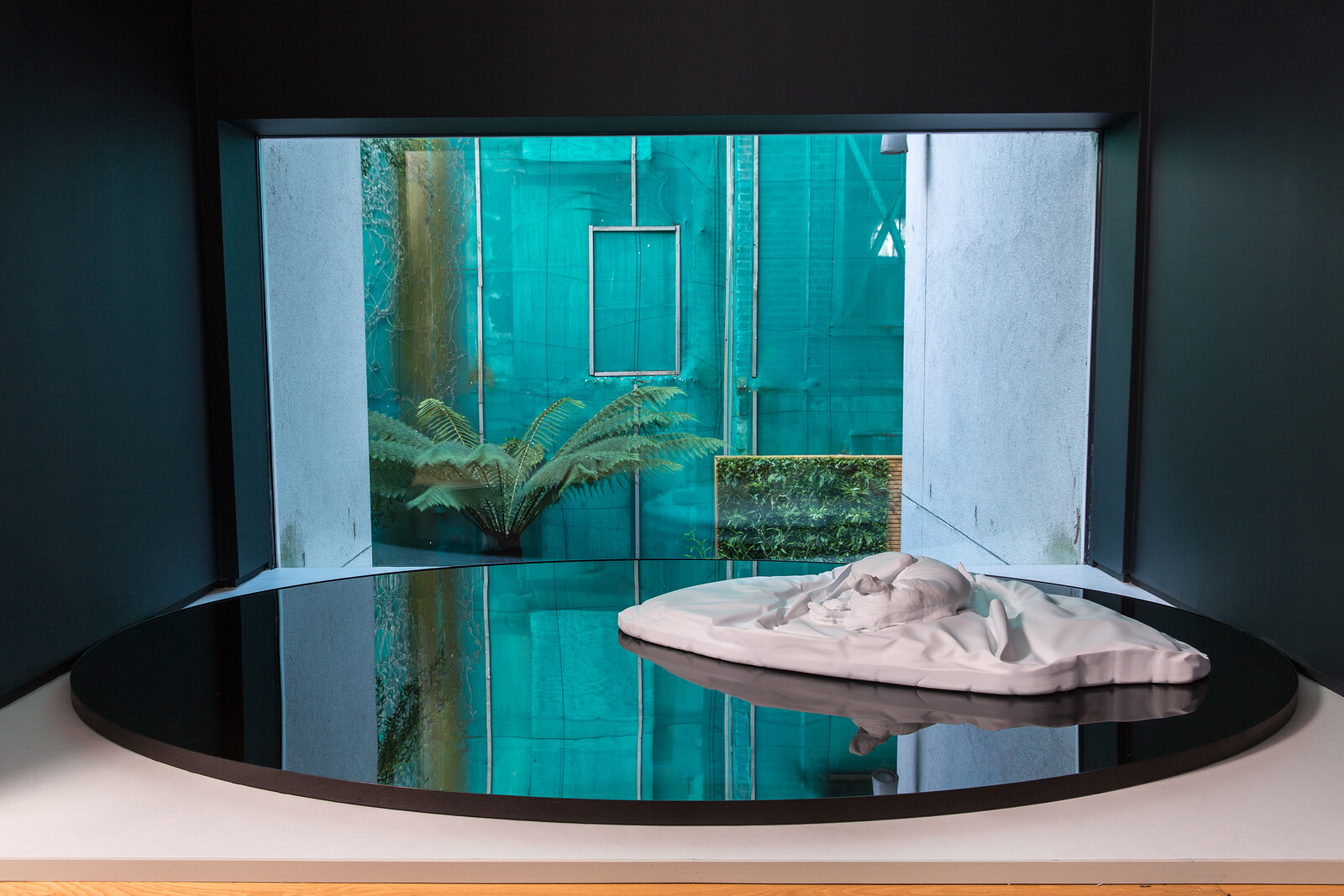
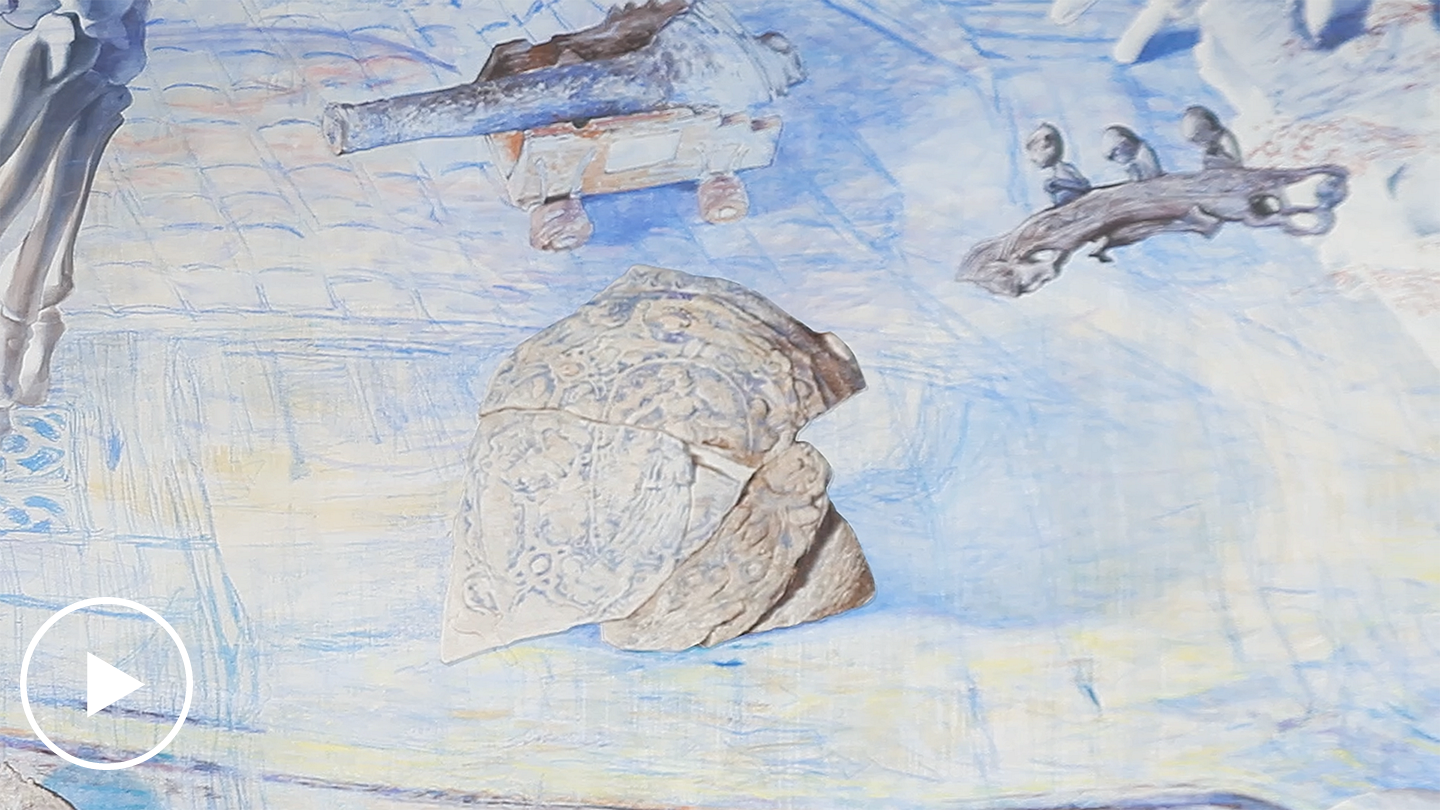
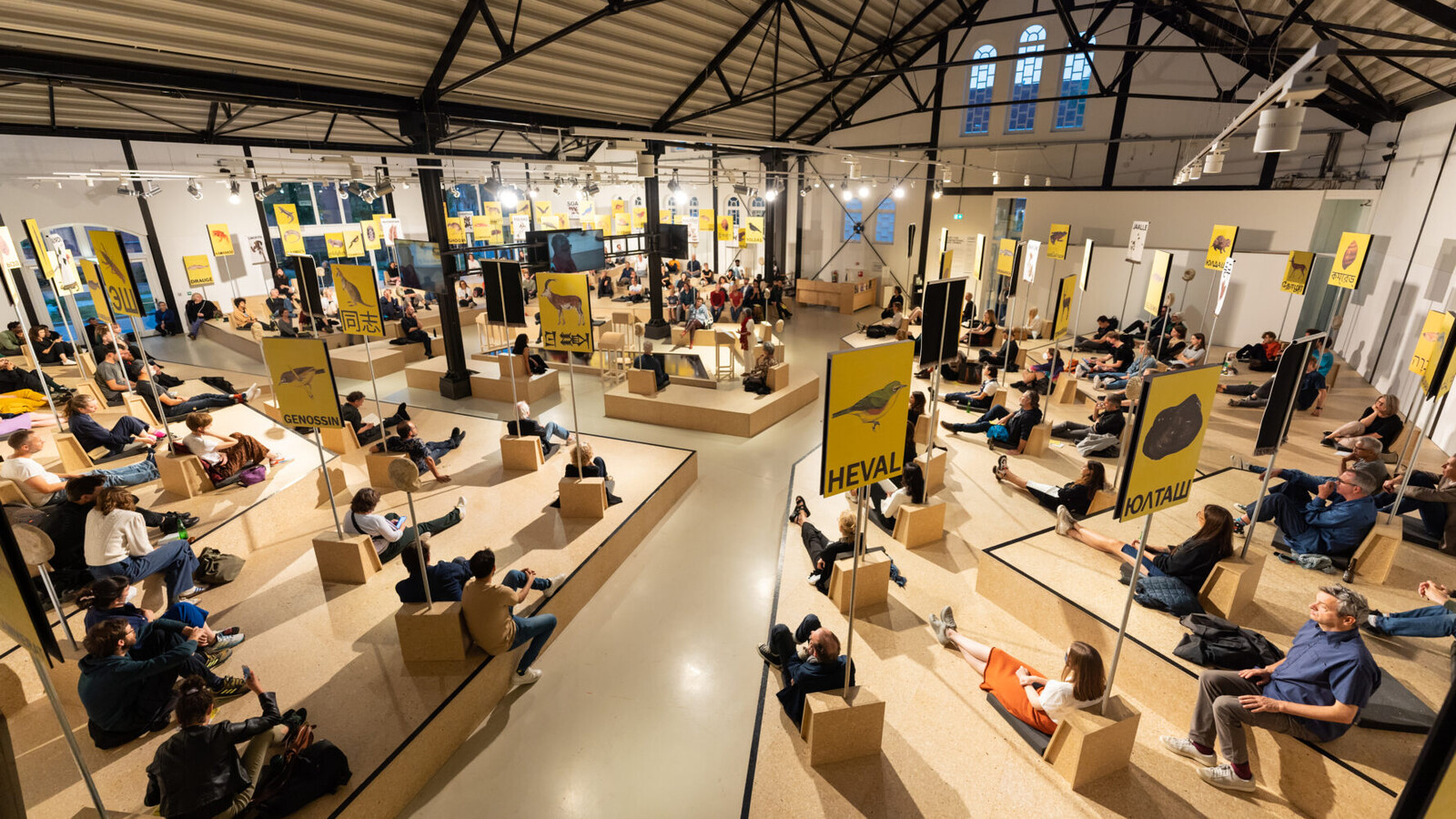
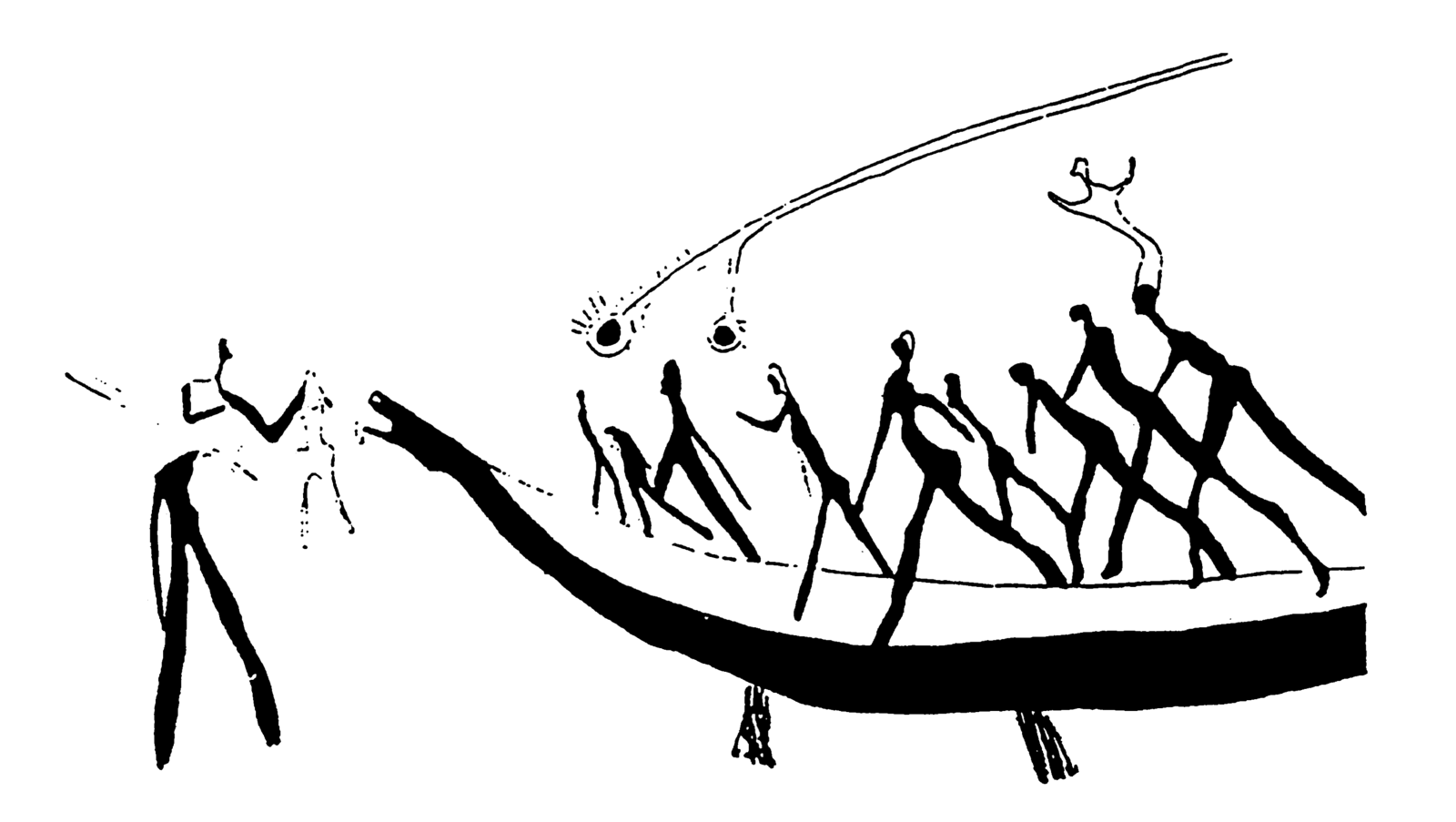
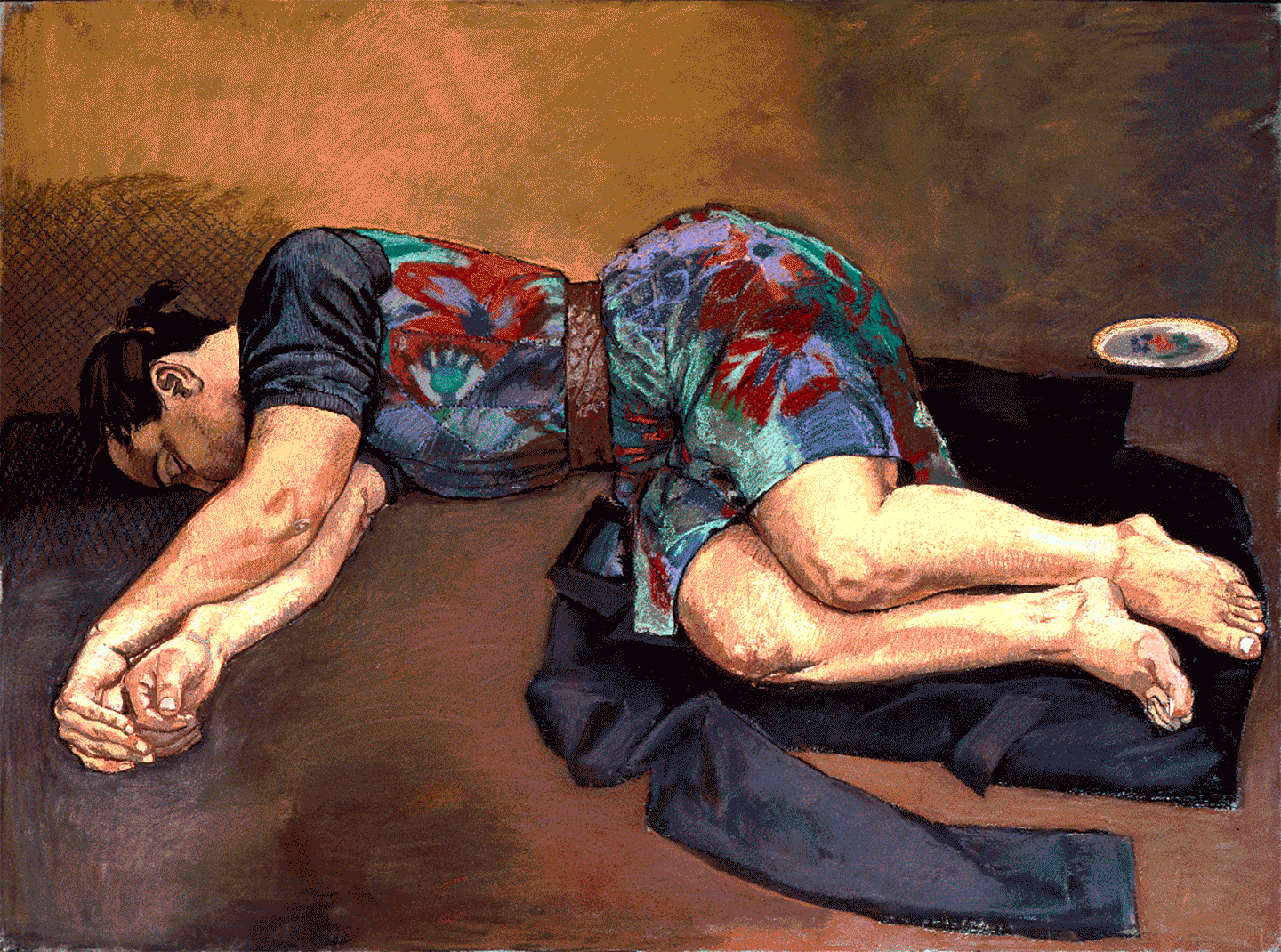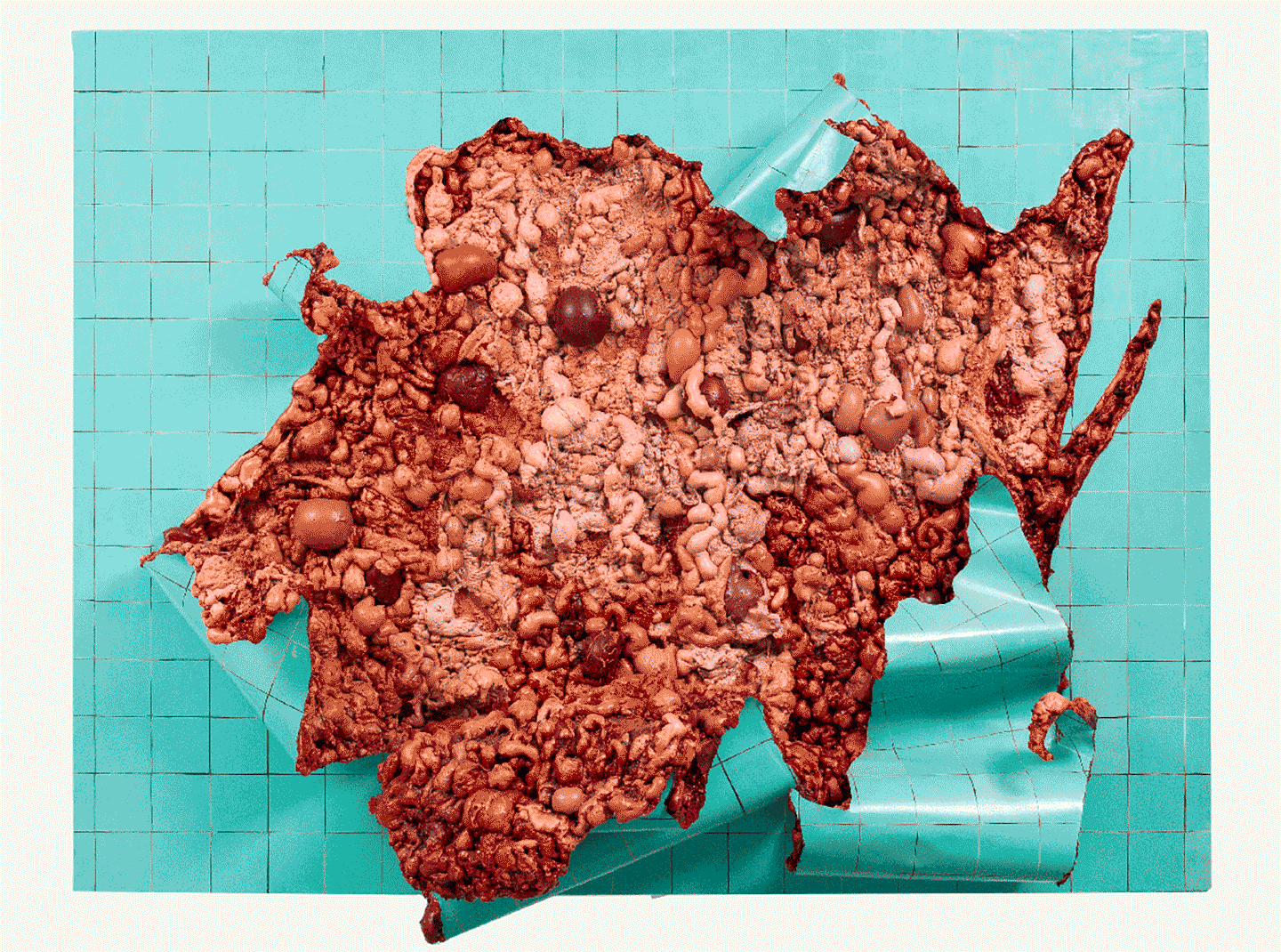“It Would be Alright if He Changed My Name”: Maxime Jean-Baptiste with World Records
For Okwui Enwezor, the void of Ground Zero indexes the full manifestation of a Fanonian “tabula rasa” in which the entropic unleashing of excessive violence weakens and dissolves the “dead certainties” of the formerly stable Western liberal/imperial global order. Such systemic crises present an unforeseen possibility for the global majority, a “founding moment,” wherein subsequent structural reconfigurations allow for their demands to be more fully articulated. These articulated demands necessarily include artistic and cultural responses, which, Enwezor observes, “posit a radical departure from the system of hegemony that fuels the present struggle.”
The origins and development of nationalist movements have to be examined from the perspective of the geopolitics among major empires, rather than by building half-baked theories based on weaker sociopolitical forces such as ethnic identity, historical memory, the pursuit of national consciousness, advancements in communication and information exchange, and the diffusion of the nation-state political model. I am not suggesting that these latter factors are unimportant, rather that their role in shaping nationalist movements is first and foremost determined by the geopolitics of major empires.
The advanced tools used to sequence, model, and analyze biological data provide unprecedented insight into the intricacies of life, yet they also reveal the boundaries of mechanistic certainty. As more aspects of the biological world become “datafiable,” vast amounts of information resist neat conclusions. Knowledge spills beyond singular narratives, challenging the models meant to contain it. Within these gaps—where data resists synthesis and certainty appears layered—it becomes necessary to ask what it means to know, and how human understanding fits into a universe that may never fully reveal itself.